Do you get exhausted easily? Do you get palpitations very often? Do your muscles feel sore and weak? Well,then there is a great likelihood that you could be a victim of one of the vitamin deficiencies.
Over the past few years, our lifestyle has changed tremendously. Skipping meals, increased intake of caffeine containing beverages,sedentary lifestyle,decreased exposure to sunlight – all these factors are not just responsible for the increasing incidence of obesity and diabetes in the population but also for many deficiency diseases.Vitamin B12 and Vitamin D are the two common deficiencies that could lead to a myriad of health problems.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency is a condition in which the body has inadequate stores of Vitamin B12. This deficiency is much more common than was previously believed.
Vitamin B12, also called as cobalamin, is involved in a number of key body processes. However, it plays a key role in the red blood cell production,functions of nervous system, sperm production, normal growth and adequate functioning of the immune system. It also improves memory and concentration,prevents cancer and protects the body against allergies and toxins.
Signs & symptoms
- Fatigue, weakness and pallor
- Dizziness and fainting
- Irritability
- Depression
- Menstrual problems
- Shortness of breath
- Tingling and numbness of the feet
- Palpitations
- Poor appetite
Factors Leading to Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency could result from inadequate dietary intake of vitamin B12 as it occurs naturally only in animal products. Children are at primary risk for developing this deficiency since they have less vitamin store in their body. Besides, pernicious anaemia and intrinsic factor deficiency can also lead to vitamin B12 deficiency in adults. Also, vitamin B12 deficiency is far more common in elderly people and vegetarians.
Getting Your B 12 Levels Right
The diagnosis for this deficiency can be confirmed by serum B12 levels. The lowest acceptable level is 200 picogram/mililitre (pg/ml) – 550 pg/ml.With prompt diagnosis and treatment, Vitamin B12 deficiency is treatable and has good prognosis with a minimal risk of developing serious complications, such as nerve damage, anaemia or dementia.
Treatment of vitamin B12deficiency involves replacing the body’s depleted stores of vitamin B12. Oral vitamin B12 replacement therapy is prescribed in some cases. However,to ensure maximum absorption, it can also be administered intramuscularly via injections.Also,including portions of red meat, poultry, fish and dairy products in your diet will also help.
Vitamin b12 facts
- Vitamin B12 is a water soluble vitamin. It is an essential vitamin for humans as it can not be naturally produced by the body. Therefore, vitamin B12 has to be obtained from food or supplements
- Vitamin B12 levels in the body may get affected due to excessive intake of alcohol and use of medicines like antibiotics, antacids & some diabetic medications. Nicotine can also lower serum levels of B12
- Older adults and strict vegetarians should make sure that they get enough vitamin B12 by including fortified foods or supplements in their diet
Food Sources For Vitamin B12
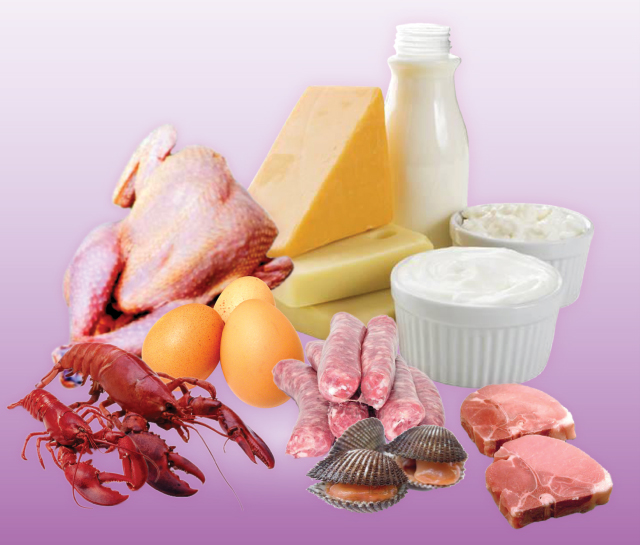

- B12 is also added to the fortified grain products, such as cereals
- Eggs, Meat, Poultry, Shellfish, Fish, Milk
Dietary reference intakes For vitamin b 12
Infants: 0.4 – 0.5 micogram (µg)/day
1- 8 years of age: 0.9 – 1.2 µg/day
9 – 70 years of age: 2.4 µg/day
Pregnancy: 2.6 µg/day
Lactation: 2.8 µg/day
People at risk
- Vegetarians who do not take vitamin supplements
- Pregnant or breast-feeding women who are vegetarians
- Breast-feeding infants of mothers who are vegetarians
- People with digestive problems (like intestinal infections) or Pernicious Anaemia
Research highlights
- Recent studies indicate that B12 deficiency is far more widespread than believed. It is proposed that 600pg/ml is the criterion for low level rather than 350 pg/ml which was earlier.
- Research shows that dark skinned people living in the temperate climate have low vitamin D levels as melanin in the skin hinders vitamin D synthesis.
Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D (calciferol) belongs to a group of fat soluble secosteroids.In humans, Vitamin D is unique because of its functions as a prohormone as well as its synthesis to Vitamin D3 in the body when exposed to adequate sunlight.
Vitamin D regulates the concentration of calcium and phosphate in the body and promotes healthy growth and remodelling of the bone. Vitamin D prevents rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults. Along with calcium, it protects elder adults from osteoporosis.
Vitamin D also affects neuromuscular functions, causes inflammation and influences the action of many genes that regulate proliferation and apoptosis of the cells. Vitamin D is also essential for the healthy growth of hair follicle as well as for a healthy immune system. Vitamin D deficiency is the main cause of rickets in young infants because breast milk is low in vitamin D and so is the cereal based diet.
Vitamin D & Bones
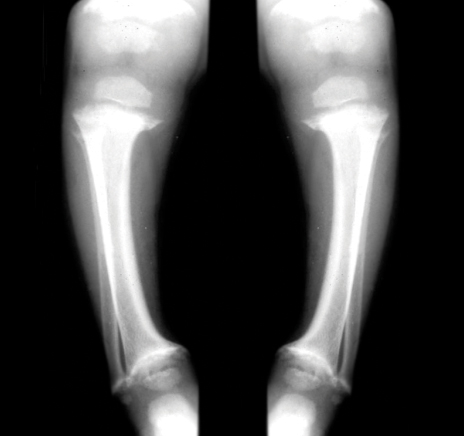
Vitamin D deficiency is known to cause several bone diseases like:
- Rickets,a childhood disease characterised by impeded growth and deformity of the long bones.The earliest sign of subclinical vitamin D deficiency is abnormal softening or thinning of the skull
- Osteomalacia, a bone-thinning disorder that occurs exclusively in adults, and is characterised by proximal muscle weakness and bone fragility
- Osteoporosis, a condition characterised by reduced bone mineral density and increased bone fragility
Did you know?

Human body makes vitamin D when the skin is directly exposed to the sunlight. That is why vitamin D is often called as the ‘sunshine’ vitamin. Ten to fifteen minutes of sunshine three times weekly is sufficient to meet your body’s vitamin D requirement. Most people meet at least some of their vitamin D needs this way.
Managing Vitamin D Deficiency
25 hydroxyvitamin D level of 20 ng/ml (nanogram/mililitre) in serum is desirable for bone and overall health. Vitamin D intake lower than 100 International Unit (IU)/day is associated with increased risk of hip fracture.
Oral vitamin D replacement or intramuscular injections are prescribed to treat Vitamin D deficiency
Signs & symptoms
- Poor growth in children
- Delayed tooth formation
- Dental deformities
- Tingling
- Weakness
- Muscle cramps
- Bone pain
- Spine and other bone deformities
- Stooped posture and loss of height
Vitamin d facts
- Without sufficient vitamin D, which is crucial for calcium absorption in your intestines, your body cannot absorb calcium, thus rendering calcium supplements useless
- Sunscreens, even the ones like SPF-8 block your body’s ability to generate vitamin D by 95%. Therefore, sunscreen products can create critical vitamin deficiency in the body
- Natural sunlight rays responsible for generating vitamin D in your skin cannot penetrate glass. Therefore, your body can not generate vitamin D from the sunlight you receive while sitting in your car or home
Food Sources For Vitamin D

- The body itself makes Vitamin D when exposed to the sun
- Cod Liver Oil, Eggs, Oysters, Mushrooms, Cheese, Butter, Cream, Fortified Milk, Fish and Fortified Cereals
Dietary reference intakes For vitamin D
For Infants: 400 IU/day
1 – 70 years of age: 600 IU/day
71 years & above: 800 IU/day
Pregnancy: 600 IU/day
Lactation: 600 IU/day
People at risk
- Naturally dark skinned people
- Elderly & people who are housebound
- People who cover their skin for religious or cultural reasons
- Babies & infants of vitamin D deficient mothers,especially breast fed babies
 Back to Site
Back to Site