There are around 33 million people with diabetes – mostly type 2. However,only 12-14% of all the patients get treated. Therefore, it is very important to create awareness as only correct information will help in better control and management of diabetes.
How does one get diabetes?
- Type 1 Diabetes
Results from the body’s failure to produce insulin, and requires the person to inject insulin - Type 2 Diabetes
Results when pancreas do not produce enough insulin to control glucose levels or the cells Stop responding to insulin - Gestational Diabetes
Results when the body of a pregnant woman does not secrete excess insulin required during pregnancy leading to increased blood sugar levels
Managing Diabetes
While highly manageable, both type 1 and type 2 diabetes may cause severe damage to health of an individual if not managed
properly.People with either type of diabetes are at risk of damage to their eyes, kidneys and feet with advancing age. However, the risk of developing these complications can be greatly reduced with good control of blood glucose.
For most people, type 2 diabetes is a progressive disease. When first diagnosed, many people with type 2 diabetes can keep their blood glucose at a healthy level with oral medications. But over time, the body gradually produces less and less of its own insulin,and eventually oral medications may not be enough to keep blood glucose levels normal. Due to the natural development of the condition, many people with type 2 diabetes eventually require insulin treatment. If insulin is started early enough many of the serious complications may be avoided.
Besides medications,a well charted diet and planned exercise regime plays a significant role in normalisation of the blood glucose levels. Also, people with diabetes should have regular checks of their blood glucose levels, blood pressure, eyes, feet,
kidneys and heart so that any change can be detected and treated well in time.
Set your goals!
- Blood Glucose Profile Fasting <100mg/dl PPG <140 mg/dl HbA1c <7%
- Cholesterols – LDL <=100
- Blood Pressure – 120/80 mm/Hg
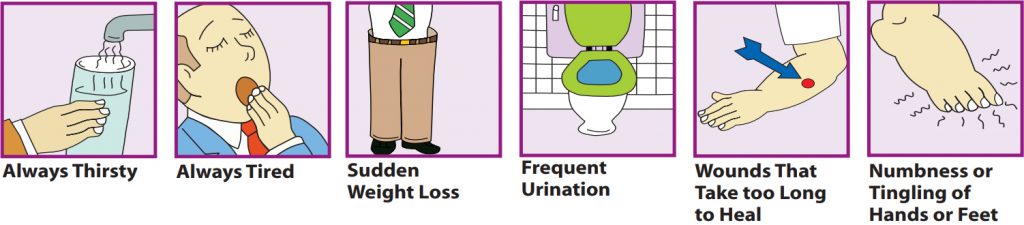
Did you know?
- 40% of diabetic patients will develop End Stage Kidney Disease over a period of 20 to 25 years leaving the person in need of either a kidney transplant or dialysis
– Diabetes could cost you your kidneys.
– If you are a diabetic, get your creatinine levels checked annually. - 5 to 10% of diabetic patients will develop Retinopathy over a period of 10 years.
– Don’t wait until you develop blurred vision.
– If you are a diabetic, get your eyes checked once a year. - 2 to 3 out of 100 diabetic patients undergo lower limb amputation. In a diabetic patient the risk of a lower limb amputation is 40 times higher than in a normal person.
– Don’t wait until you get a foot ulcer.
– If you are a diabetic, get your feet checked regularly.
Foot care for Diabetics
People with diabetes can develop many complications including several foot problems. Even ordinary complaints can rapidly worsen and lead to serious complications. If this happens to the feet, it may result in deformity, disability or even amputation.
However,the good news is that with regular visits to the doctor and proper foot care, most of these problems can be prevented.
What Happens To The Feet In Diabetes?
Usually in diabetics the nerves get numb, so one often fails to notice injury as there is no pain felt. The sense of temperature is also lost,therefore, one might not feel hot water or hot tiles while walking bare feet. Feet may get deformed, altering the mechanics of weight bearing, thus, exposing the areas of the feet to abnormally high pressures which results in breakdown of the skin.
Further more, the wound healing mechanisms are also affected, leading to prolonged time in healing of the wounds. Adding to the problem is the fact that 20% of diabetics with foot problems have narrowed or blocked blood vessels in their feet. This further impairs the healing process as adequate blood flow is required for healing any wound.
What Should I Do If I Am A Diabetic With Foot Problem?
- Clean the wound with dilute Savlon or Dettol
- Cover the wound with sterile gauze
- Check your blood sugar levels
- Make sure your affected foot does not get wet. Use plastic bag to cover the foot
- Contact your doctor immediately and/or seek an appointment with the DIABETIC FOOT CLINIC
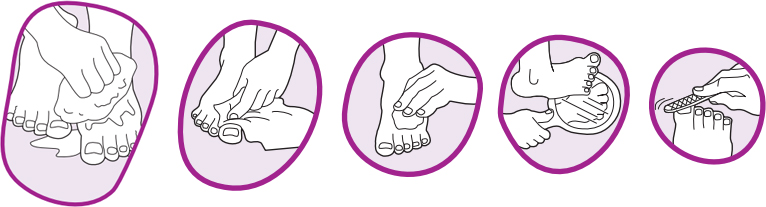
- Wash your feet everyday. Never soak your feet in water for too long.
- Use a soft towel for drying. Make sure you dry in between your toes too.
- Rub a thin coat of skin lotion over the top and bottom of your foot.
- Check your feet everyday under enough lighting for cuts, scratches, pain and tenderness.
- Trim your toe nails every week.
Foot care advice
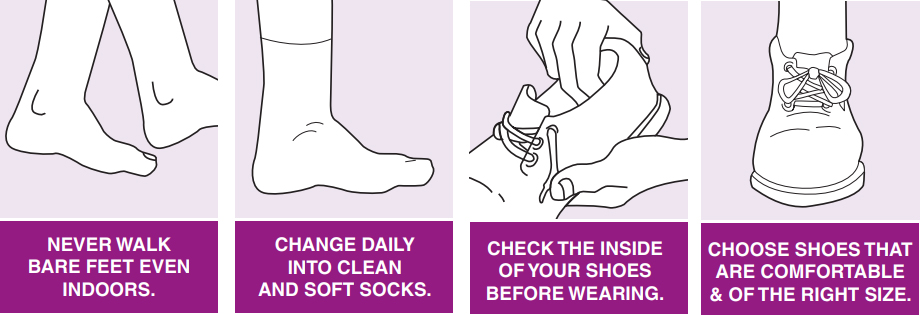
- Shoes should cover & protect the feet
- Avoid pointed,high heels shoes
- Go for shoe shopping in the evening
- Break in new shoes gradually to avoid blisters
- Use clean,dry seamless socks/stockings of right size
- Wear comfortable footwear at home
Know your symptoms
People at risk
- Obesity
- Sedentary Lifestyle
- Unhealthy Eating Habits
- Family History and Genetics
- Increased Age
- High Blood Pressure
- High Cholesterol
- History of Gestational Diabetes
If D for Diabetes, Then…
- A: A1c (Glycosylated Haemoglobin)
- B: Blood Pressure Control
- C: Cholesterol Management
- D: Drugs & Diet Therapy
- E: Exercise Schedules
- F: Follow ups
Be a smart traveller!
Travel Kit Must Haves
- Emergency ID Card
- Blood Glucose Meter, Lancets, Test Strips,Log Book & Prescribed Medicines
- Blood Pressure Kit
- Handful of Fast Acting Sweets
- Breathable All Cotton Socks
- Comfortable Walking Shoes

 Back to Site
Back to Site