Dehydration is a common medical emergency in children and usually results from acute diarrhoea. It is estimated that around 1000 children die of diarrhoea and dehydration every day in India. Let’s find out how we can prevent little ones from these debilitating episodes.
Diarrhoea
Diarrhoea is defined as passage of three or more liquid stools in 24 hours. Infants, particularly breast fed babies pass watery stools after every feed; this should not be mistaken for diarrhoea.
Parents should watch for signs of dehydration. Dehydration usually happens in children who are having very frequent watery stools, who are repeatedly vomiting or those who are not given any oral rehydration or are given the wrong solutions.
Most diarrhoea in children is viral and hence no specific therapy is indicated. Antibiotics are indicated only when there is visible blood in stool. Use of antibiotics in viral diarrhoea is of no use and may lead to antibiotic resistance.
Diarrhoea in children may need supportive care like anti vomiting medication. There is some data to support the use of zinc and probiotics in childhood diarrhoea. Antimotility agents, which are commonly used in adult diarrhoea, should be avoided in
children.
Feeding should be continued during diarrhoea as frequent small meals to avoid malnutrition. Most importantly, prevention of dehydration is the crux in the treatment of diarrhoea.
Prevention
- People caring for sick children or adults should wash their hands carefully after changing diapers or helping an individual use bathroom
- Children should be instructed to wash their hands frequently, especially after using the bathroom
- Practice safe food-handling. Always wash hands before and after handling food
- Raw vegetables and fruits should be rinsed thoroughly in clean water
- Food should be cooked properly to the right temperature
- Always store and serve food in clean utensils
- Do not consume foods from hawkers
- Breast feeding and timely weaning should be encouraged
- Use oral rehydration solution for adequate rehydration
- If travelling, be careful while deciding on the restaurants and selecting food
- Unrestricted use of antibiotics in the management of diarrhoea should be discouraged
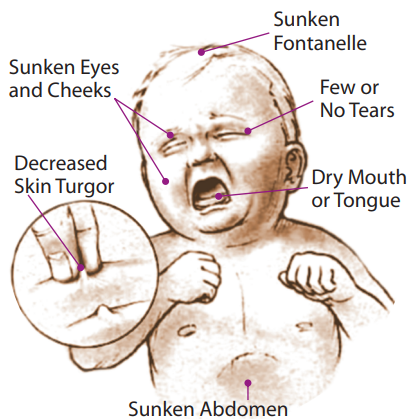
Degree of dehydration
Fluid loss of 5% of the body weight is considered mild dehydration (no symptoms),10% is moderate (some symptoms),& 15% or more is severe dehydration (pronounced symptoms).
| Symptoms | No | Some | Pronounced |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eyes | Normal | Sunken | Very Sunken & Dry |
| Mouth & Tongue | Moist | Dry | Very Dry |
| Thirst | Drinks Normally, Not Thirsty | Thirsty, Drinks Eagerly | Drinks Poorly or unable to drink |
| Heart Rate | Normal with normal pulses and breathing & warm extremities | Increased with rapid pulses, fast breathing & cold extremities | Increase with weak pulses, deep breathing & cool mottled extremities |
| Skin Turgor Test | Instant recoil | Recoils in < 2 seconds | Recoils in >2 seconds |
| Condition | Alert | Restless & Irritable | Lethargic or Unconcious |
| CAUTION | Take Immediate Precautions | Call Your Paediatrician | Immediate Medical Attention Required |
Water – An Essential Element
Water comprises about three quarters of the human mass and is a major component in every cell. Water consumption varies with the size and activity level of the person as well as with the climatic conditions.
Stay hydrated
- People should drink at least eight glasses of water a day and more if they sweat a lot. One should also drink plenty of water before,during and after exercise
- Do not drink coffee,colas,or other drinks that contain caffeine.They increase urine output and make you dehydrate faster. Keep a bottle of water on your desk so that you can drink frequently
- Eat foods with high water content like grapefruit, strawberry, watermelon, cabbage, cauliflower, cucumber, eggplant, lettuce, radish, spinach and tomato. Soup and popsicle are also high in water content
- Yogurt contains substantial amounts of potassium and sodium, which will help replace the electrolytes that have been lost
Effect of water on the human body

- Regulates Body Temperature
- Lubricates Joints
- Protects Body Organs and Tissues
- Prevents Constipation
- Helps in Flushing Out Waste Products
- Carries Nutrients & Oxygen to the Tissues
Did you know?
- Besides diarrhoea, dehydration can also occur when the total amount of fluid lost through sweating,urination and/or vomiting is more than the amount of fluid consumed
- It is important to keep in mind that children are often dehydrated before symptoms appear. There fore, prevention by hydrating before, during and after play is very important
- Dehydration not only hurts performance but can put a child at risk of heat-related illness, such as heat cramps, heat exhaustion, or may be even heat stroke
Detecting dehydration
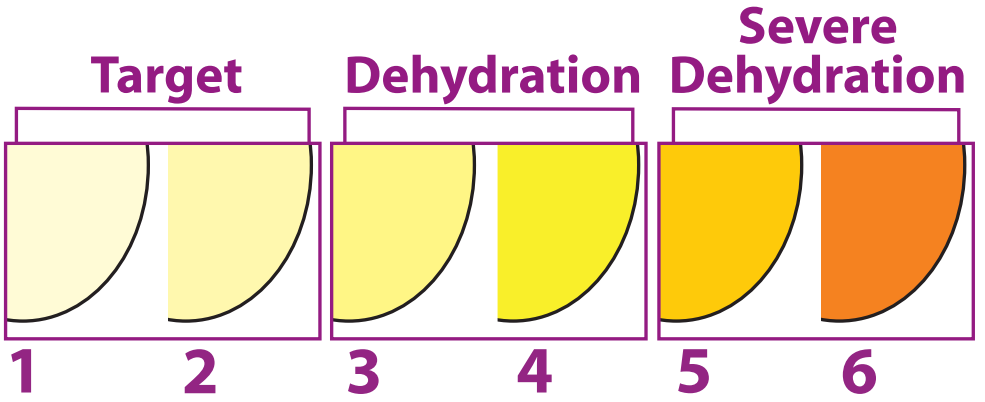
Urine colour is an indicator of hydration status. If the colour of urine is:
- Light like lemonade then the child is likely to be hydrated
- Dark like apple juice then he/she is likely to be dehydrated
Skin turgor test
Skin Turgor is a sign used to assess the degree of dehydration. The skin on the back of the hand, lower arm or abdomen is grasped between two fingers so that it is tented up. The skin is held for a few seconds then released.
Normal Turgor: Skin will recoil rapidly back to its normal position.
Decreased Turgor: Skin remains elevated and recoils slowly to its normal position.
Rehydration
Dehydration can be prevented and treated with Oral Rehydration Solutions (ORS). It is said that ORS has been the most cost effective strategy in the past century which has saved more lives than any other healthcare intervention.
What is ORS?
ORS is a mixture of common salt with potassium salts, glucose and sodium citrate. Besides commercially available ORS, appropriate ORS substitutes include coconut water, homemade sugar salt solution, rice kanji, etc. Fruit juices, fizzy drinks and plain glucose solution are not the right ORS substitutes and should not be used.
How to Prepare ORS at Home?
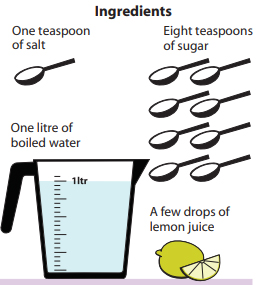
Preparation Method: Stir the mixture till the salt and sugar dissolve. Be very careful of the correct amounts. Too much sugar can make the diarrhoea worse and too much salt can be extremely harmful to the child. The drink should taste less salty than tears.
Serve: Feed ORS to the child from a clean cup. Do not use a bottle. ORS should be given slowly, 1-2 spoons every few minutes,to reduce the risk of vomiting.
Remember
Some children especially those with very frequent stools, repeated vomiting and severe dehydration will require intravenous hydration. Therefore, if dehydration is suspected the child should be taken immediately to the nearest healthcare facility and should be given ORS during transportation.
 Back to Site
Back to Site