Stroke or brain attack results from sudden interruption of blood supply to the brain. If the blood supply is stopped for more than a few seconds brain cells start dying due to lack of oxygen and other nutrients.Stroke can also result from rupture of a blood vessel,leading to the damage of brain cells.The symptoms of stroke occur suddenly and depend on the part of the brain affected.
WHEN STROKE OCCURS
DO’S
- If you or someone you know develops the warning signs of stroke, immediately seek medical help and rush the person to the hospital
- Stroke is treatable but only if stroke is recognised in time
- Rush to the hospital even if symptoms recover, as these could be a warning of an impending severe stroke or brain attack
DON’TS
- Do not try to diagnose a stroke yourself
- Do not wait to see if symptoms recover
- Do not take aspirin, blood pressure or any other medications to try treat the stroke. Medications vary according to the type of stroke and unsupervised pills may limit treatment options or worsen the stroke
- Do not wait for the doctor to come home,rush to the hospital
Types of strokes
- Ischemic stroke
Results from blockage of a blood vessel supplying the brain. This is the most common type of stroke and accounts for 80% of all strokes. - Intracerebral brain haemorrhage
Results from rupture of a brain blood vessel leading to bleeding into brain. - Subarachnoid brain haemorrhage
Results from rupture of a brain blood vessel leading to bleeding in the space surrounding the brain rather than in the brain.
What is a TIA?
In a transient ischemic attack (TIA),or a “mini -stroke”, there is a temporary interruption of the blood flow to a part of the brain. Most TIAs last only a few minutes. The warning signs of a TIA are the same as the warning signs of a stroke. TIAs are also called as “warning strokes” as they may herald a more serious stroke.
Transient Ischemic Attack
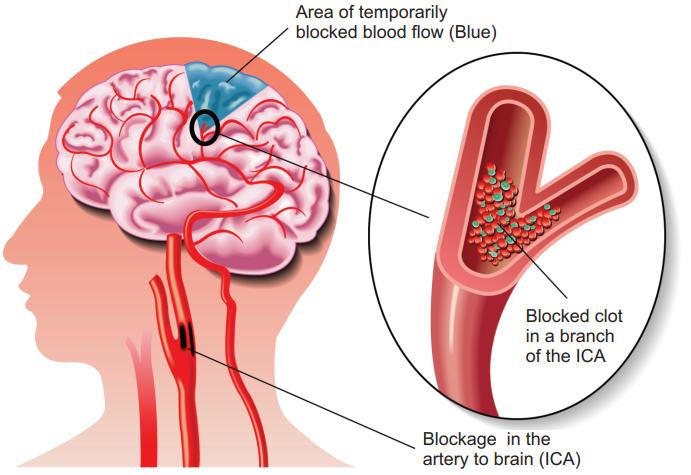
Immediate therapy after stroke
Stroke is a medical emergency as within the first few seconds of onset of symptoms, brain cells start dying. Early treatment limits degree of permanent brain damage and improves outcomes. Therefore, people who are developing stroke should be rushed to the hospital ASAP.
When a patient call/arrive KDAH, the “STROKE CODE”is immediately activated. The type of stroke and cause of stroke can be diagnosed within the first several minutes of patient’s arrival by clinical assessment, blood tests and brain scan (CT / MRI). The type of treatment given depends on the type of stroke.
ISCHEMIC STROKE
If a patient arrives within the first three hours of onset of stroke,special clot buster treatment can be given to dissolve the blockage in blood supply to the brain.Restoring the blood supply to the brain prevents ongoing brain cell death and can be lifesaving. In select persons with stroke such therapy can be given upto 4-8 hours after onset of stroke.
BRAIN HAEMORRHAGE
Various therapies can be given to prevent ongoing or repeated brain haemorrhage.
Post stroke rehabilitation
Stroke rehabilitation is started from the time the patient is admitted and tailored according to the patient’s medical condition and stroke severity. The aim of rehabilitation is to train the normal brain to take over the function of injured brain.
Stroke statistics
- WHO reports that 15 million people suffer from stroke worldwide every year.
- In India,the incidence of stroke is increasing due to hypertension,diabetes and increased smoking.
- Nearly 3/4th of all strokes occur in people aged 65 or above.
- The risk doubles each decade after the age of 55.
Risk factors in stroke
Stroke can occur at any age. While some factors are uncontrollable, many of the stroke risk factors can be largely reduced by lifestyle changes and medical treatment.
Uncontrollable Risk Factors
- Stroke is more common in people over 65
- Stroke is more common in people who have a family history of stroke
- Stroke is more common in men
- Indians have a high risk of stroke
Controllable Risk Factors
- Obesity
Work to maintain a healthy weight - Sedentary lifestyle
Engage in moderate intensity exercise - Smoking or tobacco use
Try to quit smoking or consuming tobacco in any form - Excessive alcohol intake
Alcohol consumption has to be reduced to minimal levels - Hypertension
Get it checked regularly by a doctor - Diabetes
Consult a doctor and try keeping your diabetes under control - High Cholesterol
Know your cholesterol numbers by getting screened - Previous stroke or TIA
Recognising and treating TIAs can reduce the risk of a major stroke - Heart disease
Get yourself treated for the prevailing heart diseases
STROKE is an Emergency. Every Second counts. ACT F.A.S.T!
- FACE
Does one side of the face droop? Ask the person to smile - ARMS
Is one arm weak or numb? Ask the person to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward? - SPEECH
Is the speech slurred? Ask the person to repeat a simple sentence. Is the sentence repeated correctly? - TIME
If the person shows any of these symptoms. Get to the hospital immediately
Warning signs of stroke
- Sudden weakness or numbness of one side of the body
- Sudden problems in walking
- Sudden slurring of speech
- Sudden trouble seeing
- Sudden loss of balance or coordination
- Sudden severe unexplained headache with no known cause
 Back to Site
Back to Site