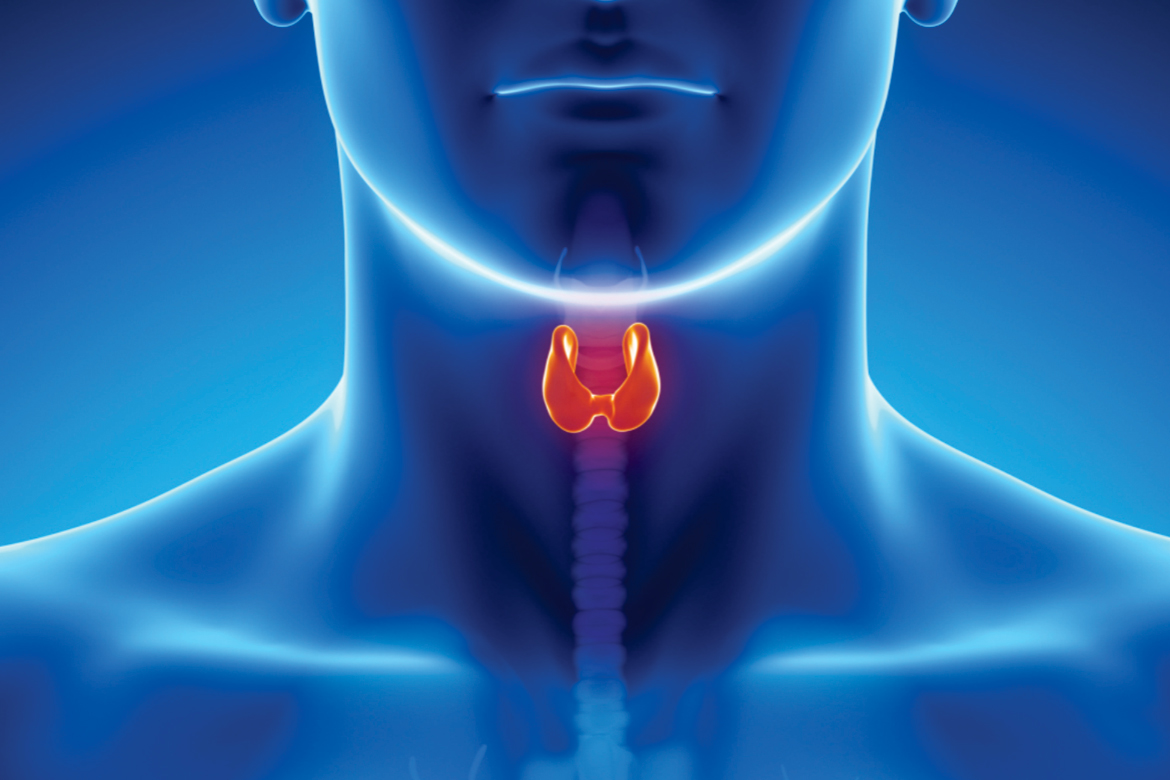
What is Thyroid Gland?
It is a butterfly shaped endocrine organ situated in the midline of the neck in the front of the wind pipe (trachea) below the Adam’s apple.
What is the function of Thyroid Gland?
- It takes up the iodine present in food and uses iodine to manufacture two hormones principally T4 ad T3.
- These two hormones T4 and T3 are then released in blood and they circulate in the entire body.
What is the function of Thyroid hormones?
T4 and T3 hormones determine / control, the metabolic rate i.e., speeds at which the body cells work,body heat and energy levels of an individual.
How is Thyroid gland controlled?
The production of T4 and T3 from the thyroid gland is under the control of the master endocrine gland called as pituitary gland which is part of the brain located in between both eyes about 2 inches deep.
The pituitary gland produces a hormone called TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) which as the name suggests,stimulates the thyroid gland to produce T4 and T3.These two hormones once reaching the upper limit of normal inhibit the further production of TSH i.e.,T4 and T3 have an inverse correlation.
How is Thyroid function measured?
Estimation of blood levels of T3, T4 and TSH would establish the function of Thyroid gland. These tests can be done at any time of the day and does not need to be in fasting state.
What are the disorders of Thyroid gland function?
Disorders of thyroid gland activity can be of 2 types –
- Underactive Thyroid gland also called as Hypothyroidism
- Overactive Thyroid gland also called as Hyperthyroidism
Myth: I cannot eat certain food if I have Hypothyoidism
Fact: Certain foods like cabbage,cauliflower,turnips,mustard have been implicated in goiter and hypothyroidism when consumed in large amounts. When your thyroid is already not functioning and you are on tablets,there is no need for any special food restriction unless you are consuming a very large amount of any particular item on a regular basis.
Myth: If I have gained weight I need to increase the dose of thyroxine for weight loss
Fact: Hypothyroidism is just one of the causes of weight gain—that too limited amount (2-5% only). If your hypothyroidism is well controlled as per your treating doctor, don’t try and overdose yourself. It is not good for your body. You need to talk to your doctor regarding modification of your diet,lifestyle and other factors responsible for your weight gain.
Myth: I can stop taking thyroxine once I feel well and my reports are normal
Fact: No. It’s important that you continue to take the medicines regularly despite feeling well. It is because the external consumption of thyroxine reports are normal.Leave the decision of changing and stopping therapy to a qualified doctor.
Myth: Taking thyroxine for long time can be harmful
Fact: No. Thyroxine when prescribed in right dosage for hypothyroidism does not cause any ill-effects.It’s a natural hormone.
Myth: Thyroxine once started needs to be taken for long time
Fact: Duration of therapy depends on the cause of hypothyroidism. In case of autoimmune mediated hypothyroidism therapy with thyroxine is usually long term
Myth: If I have Hypothyroidism I cannot conceive ever
Fact: This is a common misconception. If you neglect and don’t treat hypothyroidism, only then you have a chance of miscarriage or giving birth to a mentally retarded (cretin) baby. Individuals with Hypothyroidism if well controlled have similar chances of conceiving as those without thyroid disorder.It may be advisable to check with your endocrinologist.
Myth: I need to stop thyroxine if I am pregnant
Fact: Definitely not! If you have hypothyroidism you need to continue it throughout your pregnancy as the foetus in the womb is completely dependent on mother for its thyroxine. This is very essential for proper brain development. Consult your endocrinologist for proper dosage adjustments which can be very different during pregnancy. Taking thyroxine (for hypothyroidism) is safe during pregnancy, while stopping can be harmful.
Myth: If mother has hypothyroidism during pregnancy then offspring will also have
Fact: Certain thyroid diseases like hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism are known to run in families. The chance of offspring developing thyroid disorder is only marginally more than the normal population.
Myth: Hypothyroidism is not seen in children
Fact: It is rarer than in adults,but it can have more serious health consequences. It can result in prolonged jaundice at birth, severe constipation, mental retardation, delayed puberty, short stature, etc. Early treatment is more important in children than in an adult.
Myth: I have a thyroid swelling but my blood reports are normal
Fact: Thyroid gland function and appearance are two different aspects. Blood test helps to determine the functioning of the thyroid gland.Many times the functioning of thyroid gland maybe normal however the gland per se if enlarged needs further evaluation as it carries 10-15% chance of malignancy.
HYPOTHYROID
- Under active thyroid gland
- Decreased production of T3 &T4
- Decreased metabolism
- Decreased heart rate
- Decreased intestinal movements (constipation)
- Fatigue
- Sleepiness
- Hair fall
- Lack of sweat (dry skin)
- Weight Gain (2-5 per cent)
- Cold intolerance
- Irregular menses
Labs: T3 and T4 decreases. Thus, TSH increases
Treatment: Thyroid Hormone Replacement (T4 replacement)
HYPERTHYROID
- Over active thyroid gland
- Increased production of T3 and T4
- Increased metabolism
- Increased heart rate (palpitation)
- Increased intestinal movements (increased frequency of motions)
- Hyper irritability
- Insomnia
- Hair fall
- Increased sweating
- Weight loss (2-5 per cent)
- Heat intolerance
- Irregular menses
Labs: T3 and T4 increases. Thus TSH decreases
Treatment: Medication like Carbimazole or propylthiouracil (PTU), radioactive iodine therapy or Surgery
 Back to Site
Back to Site