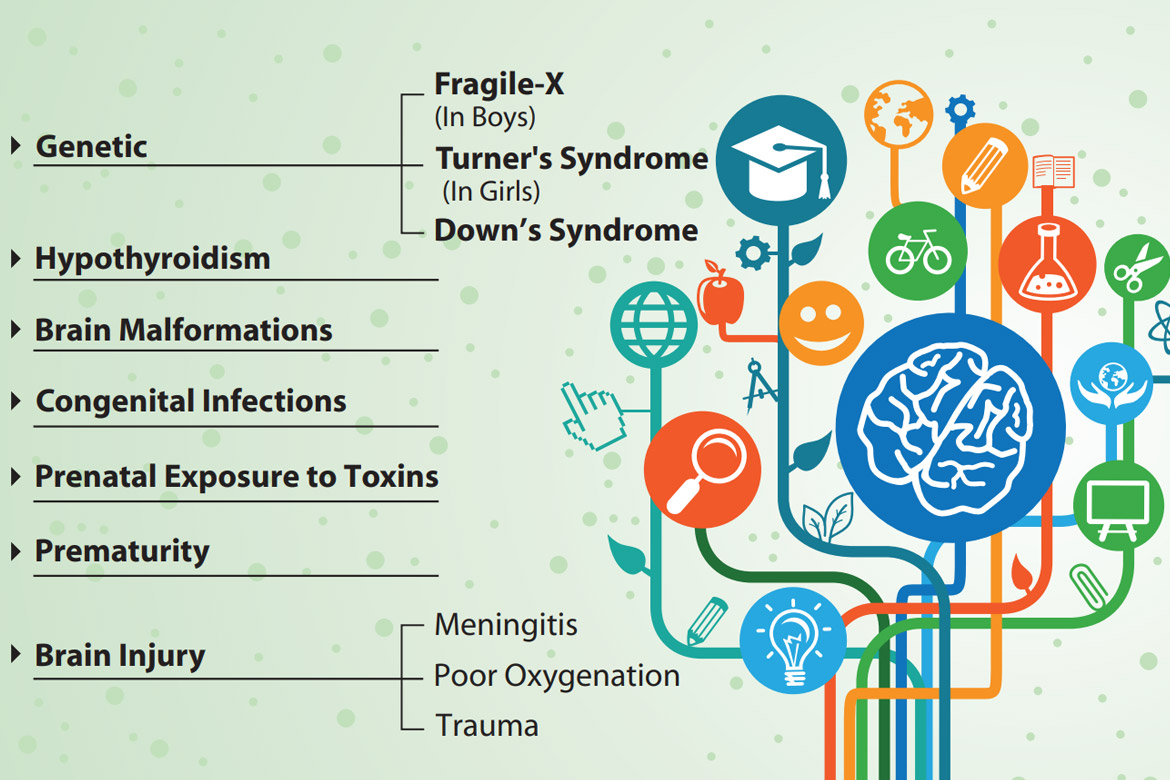
At the outset it is important to clarify that the term ‘Mental retardation’ has been discarded – instead, we use the term “Intellectual disability”. It is thought to affect about 3 percent of the population.This incidence may be higher in socially deprived communities. It means an IQ of less than 70 along with a functional impairment in daily activities apparent before 18 years of age. There are various degrees of severity – mild,moderate,severe and profound.
SIGNS & SYMPTOMS
- Language delay
This is the most common presentation. Children do not achieve meaningful speech by 18 months of age & do not speak sentences by 2 years. - Behavioural problems
These children are perceived to be hyperactive,’immature’ for age,poor social interactions,etc.Often autism and intellectual disability overlaps in the same patient. - Fine motor problems
They may exhibit the inability to do simple things like feed oneself, tie shoe laces,button or unbutton,poor drawing and later writing skills. - Academic difficulties
Schools may complain that the child is hyperactive or has poor concentration. Academic grades usually suffer. - Motor delays
Delays in sitting,walking,etc. are associated but are comparatively less severe. - Neurological abnormalities
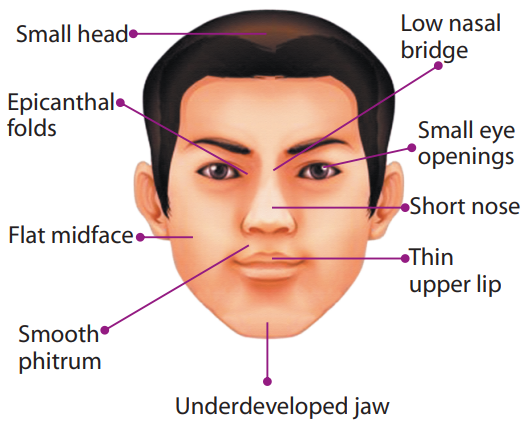
Occasionally these children may be brought to medical attention because of seizures, small or large head size, prematurity, unusual facial appearance,etc.
TREATMENT
There are no medicines which will increase a patient’s IQ.There may be medicines to treat the underlying disorder such as thyroid supplements, anti- seizure medications & others. There are also medications to improve behaviour, attention span, etc., if required. However, the backbone of treatment is neurodevelopmental therapy. This includes occupational therapy, speech therapy, special or remedial education, etc. This enables the child to fulfill his/her innate potential.The final aim is to make the individual as self sufficient as possible.
INTEGRATED APPROACH
Depending on the severity, some children can manage in mainstream schools with concessions. Concessions can be in the form of a shadow teacher, extra time in exams, dropping a few subjects,etc. Sometimes these children may require attending special schools.
The government issues certificates which state the level of intellectual disability. These can help in acquiring concessions in certain schools.Also there is ‘NIOS’- National Open Schooling system which is particularly designed to help children with intellectual disability.
HOW TO IDENTIFY?
LONG TERM PSYCHOSOCIAL RISK
People with Intellectual Disabilities Crime Victimisation
- Believe inappropriate treatment is okay
- Easy target/ victim
- False friendship
- Inability to report victimisation
- Easily influenced
- Eager to please
- Unaware of danger
- Not credible witness
- Inaccessible help
TESTS REQUIRED

Depending on the age of the child, various tests are available to measure the IQ (intellectual quotient) and social quotient. Examples are WISC-4, Wechslers’s scale, Vineland’s scale, Bayley’s etc.
The paediatric neurologist may also ask for additional blood tests including those for genetics, MRI of the brain, EEG,etc.
 Back to Site
Back to Site