Minimally invasive adrenalectomy has become the gold standard treatment of adrenal gland tumours after the initial report of laparoscopic adrenalectomy was described by Gagner et al in 1992. Multiple series have clearly demonstrated decreased pain, lower blood loss, faster convalescence, less ileus, and shorter hospit
Multiple feasibility studies have demonstrated the safety and feasibility of robotic adrenalectomy. The perceived advantages of the robotic interface include stereoscopic vision, improved magnification, and greater range of motion. As exper ience with robotic adrenalectomy has increased, robotic adrenalectomy has been used for progressively more difficult operations, including resection of large tumours, pheochromocytomas, and adrenocortical carcinomas (ACC).
Additionally, recent studies also support the role of a robotic-assisted approach during partial adrenalectomy and adrenal metastasectomy. In general, indications for adrenalectomy include hormonally active adrenal tumours, enlarging lesions, masses with concerning radiographic characteristics, and large lesions of angiomyolipoma greater than 4cm.
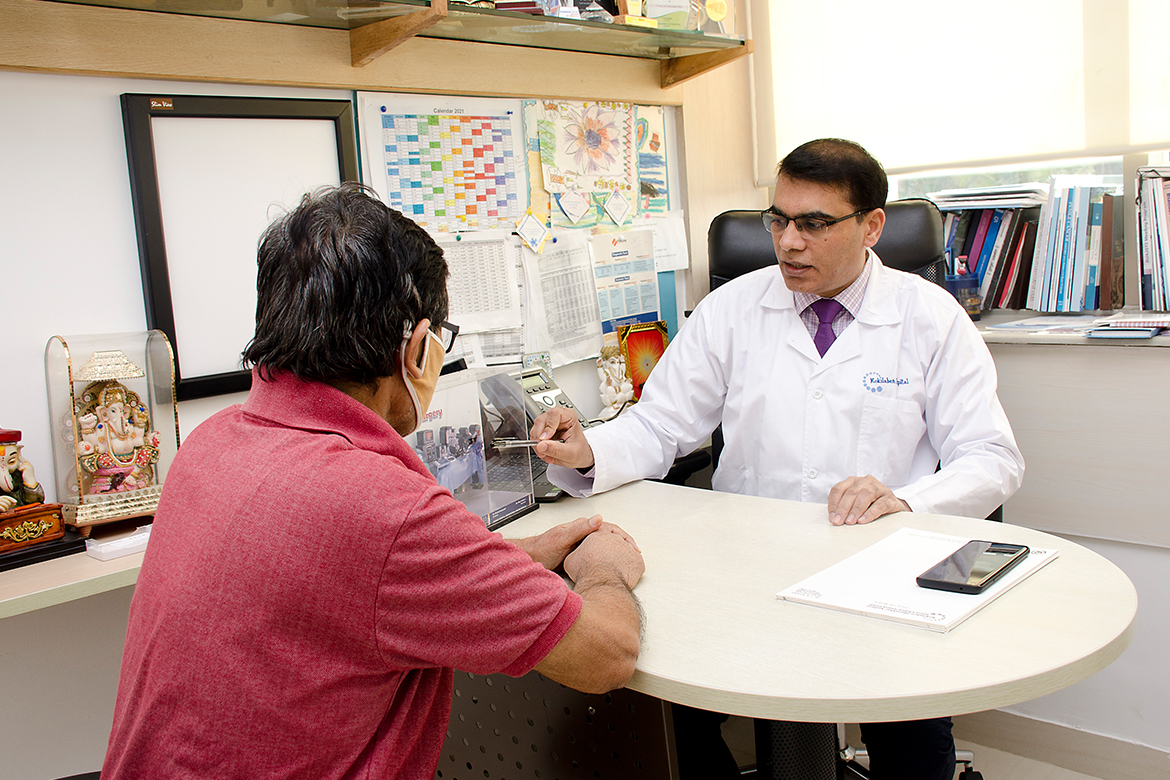
We at Kokilaben Hospital have performed more than 75 laparoscopic and robotic adrenalecto
 Back to Site
Back to Site