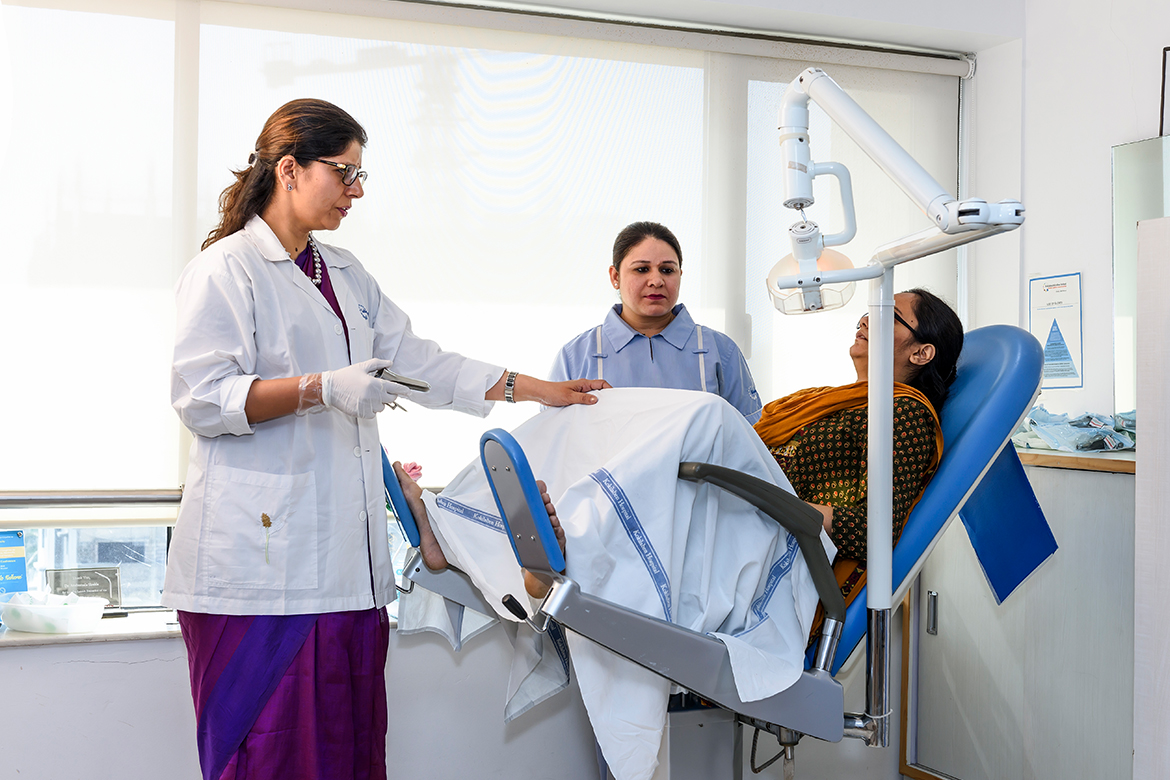
Minimally invasive surger y (MIS) has revolutionized the management of gynaecologic disorders over the last 30 years. However, the most substantial improvements have come with the advent of robotic surgery. Initially, traditional laparoscopy afforded less invasive approaches to hysterectomies, tubal ligations, adnexal surgery, and even lymphadenectomies and radical hysterectomies. However, not all surgeons are comfortable with the laparoscopic approach due to its steep and extended learning curve, nor are all patients and procedures amenable to traditional laparoscopy. In fact, the majority of advanced gynaecologic surgeries are still being performed through an abdominal incision.
Many gynaecologic surgeons are now performing procedures that they never would have been comfortable performing with traditional laparoscopy, offering many patients the option of minimally invasive surgery (MIS). The adoption of the robot has come into play in general gynecology as well as in nearly every subspecialty of gynaecology. In general gynaecology and reproductive gynaecology, the robot is being increasingly used for procedures such as hysterectomies, myomectomies, adnexal surgery, and tubal anastomosis. Also, among urogynaecology, the robot has been utilized for sacrocolpopexies and fistula repairs.
What’s Unique?
As an experienced laparoscopic surgeon, for me, almost all surgeries are felt attainable with routine laparoscopy. However, there are some aspects of robotics which on use I have felt have genuinely added to my minimal invasive surgery. The vision is far superior , its high definition with 3D which assists with difficult dissections and microsurgery. The robot system includes various scales for downscaling movements. For a scale of 10:1 for every 10cm of handle movement from the console, the robotic instruments move 1cm at the surgical site, also have tremor filtration. Intuitive hand movement refers to the movement of the robotic instruments in the same direction as the hands. The control of camera , focus and cautery is all at the console giving the surgeon complete control on the surgery even though not scrubbed.
Application in Gynaecology
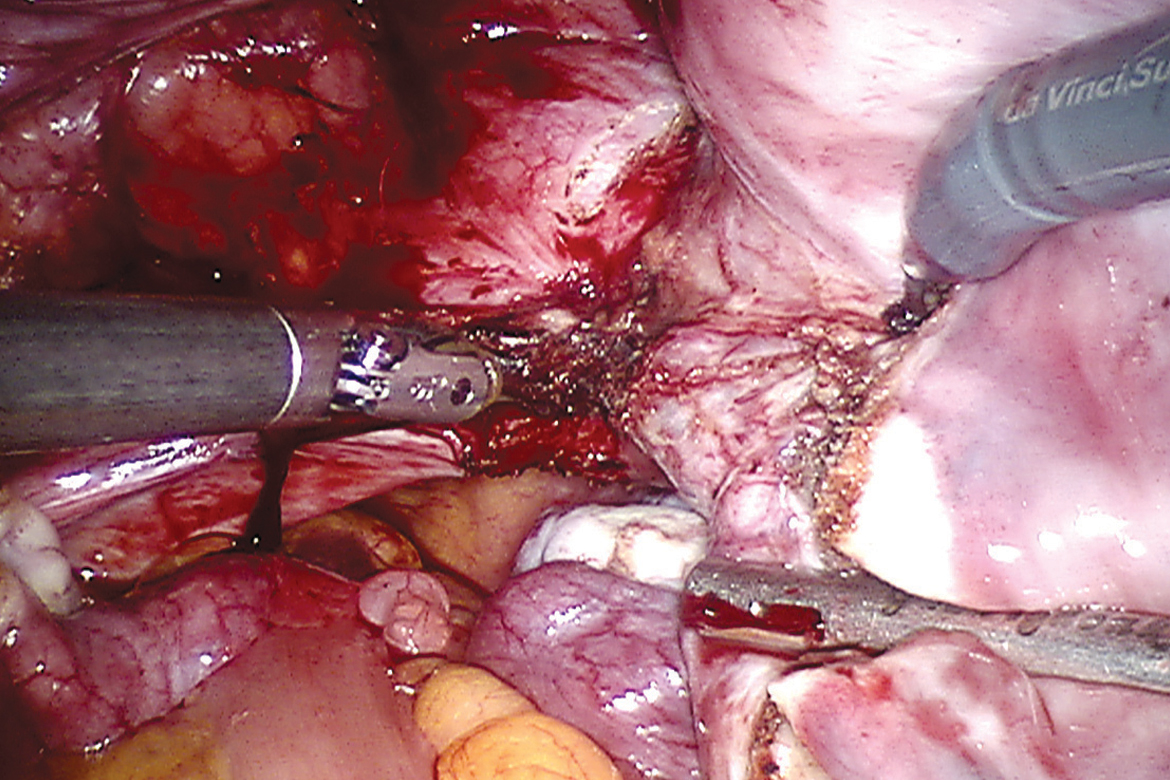
For complicated hysterectomies such as those with previous cesaerean section, endometriosis, previous abdominal surgeries, the use of robotics makes it safer with reduced rate of complications. Robotics allows myomectomies for larger number of fibroids with good approximation of the edges for maintaining integrity of the myometrium. Tubal reanastomosis surgeries benefited by robotics by allowing handling of fine sutures and needles and application of microsurgery techniques. Pelvic floor repairs requires dissection in the bony pelvis along levator ani, use of robotic arms and 3D camera allow such dissection. We are the first in western India to use robotics for sacrocolpopexy repair of vaginal vault prolapse, anterior para vaginal repair and burch colposuspension. The results of these repairs from 2 year to 6 months follow up are comparable to laparoscopy.
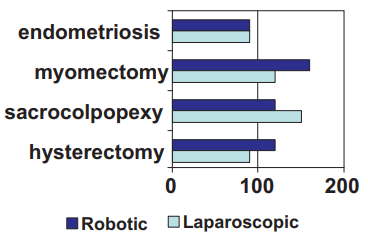
Since the last 2 years we have achieved comparable operative time and outcomes as any other benchmark in the world. Our robotic vs laparoscopic surgery time is now same. We have observed good patient acceptance of robotic surgery with improved post op recovery.
Robotic surgery has a role to play in complex gynaecological surgeries with less morbidity and complication rate.
 Back to Site
Back to Site