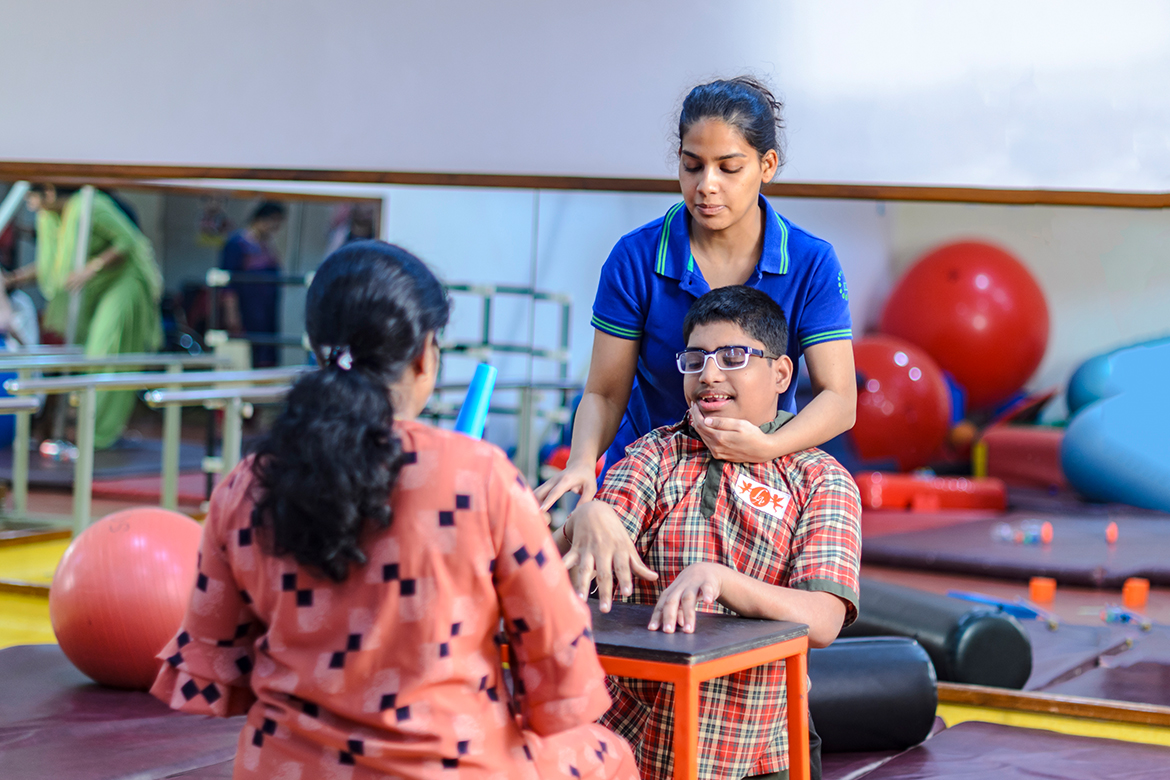
More than 200 children are born with CP everyday in India. Unfortunately, not everyone can afford specialised care due to financial constraints and lack of resources. Here, the primary care physician acts as a fulcrum in identifying and managing the disorder.
Children with CP have multisystem problems and require a multidimensional approach to manage the disease. Over the past few decades, diagnostic criteria and management algorithms for CP have seen rapid revisions in India.

The major thrust of management of cerebral palsy is to facilitate optimal functioning and encourage new learning skills; at the same time, the family needs to be provided with educational and psychological support. All this needs a team of specialists—from neurologist, physical therapist to counsellors.
However, most patients end up visiting specialised centres once and continue regular health visits to their primary care physician. In fact, sometimes it is the primary care physician who diagnoses CP and refers the child to a specialist centre for evaluation. Due to lack of resources and non-availability of specialised care, primary care physicians need to watch out for indicators, diagnose the specifi c disorder and then coordinate supportive care and psychological analysis. They play a key role in assurance, and in disseminating proper information to patients and family by forming a healthy network between
different medical professionals.
Indicators
- Diffi culties in sucking or feeding in infancy
- Delayed motor development
- Limited range of movements
- Variations in muscle tone—either too stiff or too fl oppy—exaggerated deep tendon refl exes
- Visual abnormalities, hearing defects, seizures
- Early hand preference
- Abnormal gait
How to identify a patient with CP?
Identifying Common disorders in Children with Cerebral Palsy:
Musculoskeletal system
- Increased muscle tone or stiffness (spasticity) and involuntary movements (dyskinesias) that interfere with ambulation, seating and hand function.
- Contractures, scoliosis and joint subluxations.
- Pain and cramps with irritability
Growth/nutrition
- Poor oromotor function leading to increased feeding time and recurrent aspirations
- Pain due to gastro-esophageal refl ux, and thus poor nutrition and failure to thrive
- Inability to realise hunger
- Increased caloric demand but a defi cit of calories due to the above mentioned problems
- Chronic constipation
- Dental caries
Hearing and vision
- Refractive errors, strabismus, and nystagmus
- Recurrent ear infections and speech delay
Epilepsy
- 40% of children with CP suffer from epilepsy
Behavioural diffi culties
- Attention defi cit hyperactive disorder
- Self-injurious behaviour
- Autistic traits
Other problems
- Risk of developing sores at the site of splints
- Poor bladder control with precipitancy
- Diffi culty in being able to and even maintaining sleep
- Gynaecological and endocrine issues
Therapy
- For Spasticity
Physical Therapy—Stretching exercises, positioning techniques, use of splints Medications—Baclofen, Tizanidine, Diazepam Botulinum Toxin injections Intrathecal Baclofen via pump Surgical management—Deformity correction, selective dorsal rhizotomy - Epilepsy
Appropriate anti-epileptic medication - Growth/Nutrition issues
Dietician support, screen for GERD, video-fl uoroscopy while swallowing to look for aspiration and impaired coordination and dental hygiene - Behavioural Aspects
Psychologist assessment, treatment of hyperactivity, attention defi cit, screening for autism - Addressing Issues
Improper sleep hygiene, toilet training, screening for endocrine problems
The Kdah Team
Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital is at the forefront of care for children with CP. A coordinated, comprehensive multidisciplinary medical and surgical team provides all the necessary services to diagnose and treat CP. This is provided through our team of specialists, including a paediatric neurologist and a paediatric orthopaedic surgeon who can help in managing complications, as well as supporting and counseling parents. We have a dedicated rehabilitation centre with physiatrists, and occupational and speech therapists. Parents who wish to go for another pregnancy are also encouraged to seek pre-pregnancy counselling from a Feto-maternal medicine specialist at our Advanced Fetal Care Centre. our multidisciplinary team comprising feto-maternal medicine specialist, paediatric neurologist, clinical geneticist and neuro-radiologist go through the details of the past pregnancy and childbirth, and attempt to reduce the level of anxiety for parents and other members of the family.
 Back to Site
Back to Site