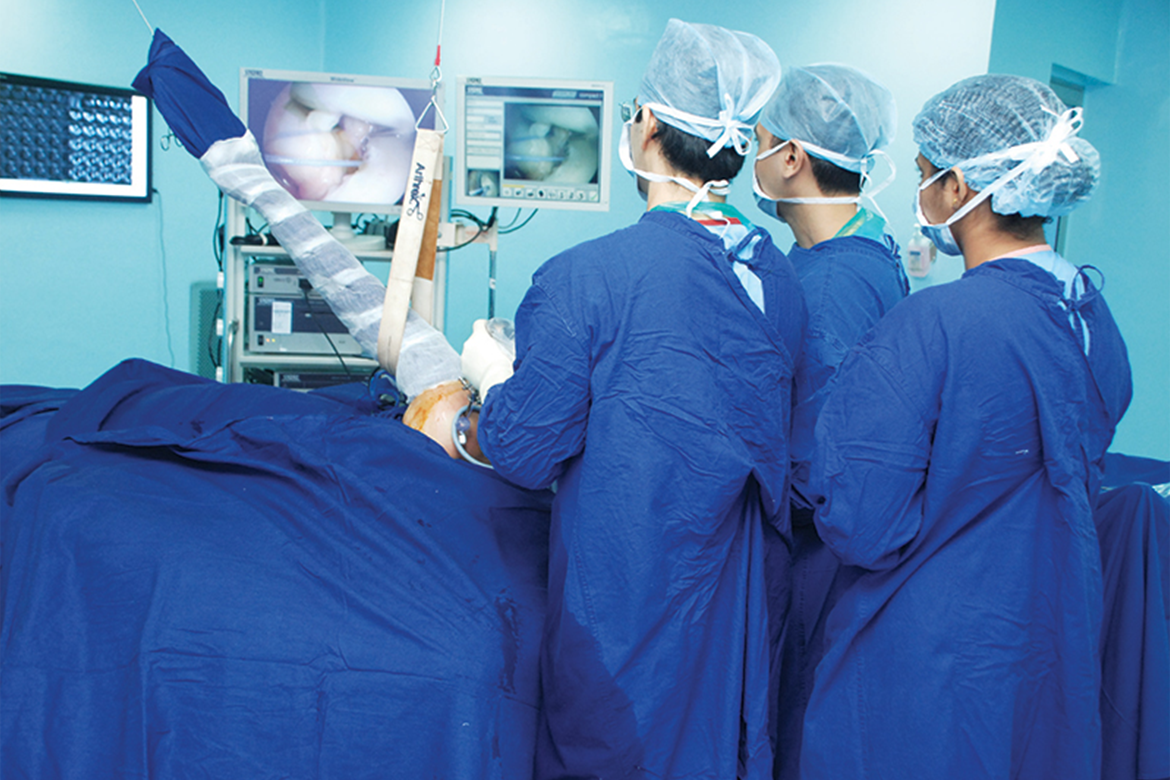
Arthroscopic surgery has grown by leaps and bounds. This minimally invasive endoscopic intervention for problems of knee and shoulder joints is now also routinely performed for the hip, ankle, elbow and wrist joints. Recent advances (such as computer navigation assisted arthroscopic knee ligament reconstruction and autologous chondrocyte transplantation for cartilage defects) have enabled sportsmen to return to their highest capabilities in the shortest possible time
Ports orthopaedics and arthroscopy have advanced hand-in-hand. Injuries in sports have been the bane of many athletes. In today’s world of competitive sports with perennial playing seasons and packed calendar, injuries are common and all the more devastating when severe. Sporting careers often depend on how well these injuries can be prevented and treated timely and optimally. Arthroscopy is often ideal and has traditionally been the only modality of treatment for injured athletes as it ensures minimal morbidity and faster recovery.
Revolutionising diagnosis management
Arthroscopic surgery has revolutionised the diagnosis and management of joint problems. Initially used only as a diagnostic tool prior to open surgery, the availability of better instruments and techniques has encouraged the use of arthroscopy for treating a variety of joint problems, avoiding complicated surgeries and longer recovery. In fact, except joint replacement and major intra-articular fractures, all other problems involving the hip, knee, ankle, shoulder, elbow and wrist joint can be treated with arthroscopic surgery.
The following are the most important recent advances in arthroscopic surgery:
- Double bundle ACL reconstruction:
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears are common knee injuries in sports. The ACL has two structurally and functionally distinct bundles, the anteromedial and posterolateral. Although the conventional ‘single-bundle’ ACL reconstruction has given satisfactory results, it is inadequate for high-demand knees in sports as they require an excessive degree of rotational stability. In order to restore anatomy and function more accurately, each of the two bundles of the ACL need to be reconstructed separately, hence the name ‘double-bundle’ ACL reconstruction. The author’s experience with this technique over the past six years has been very encouraging and the restoration of normal knee biomechanics and return to sports in elite athletes has been remarkable. - Computer navigation for arthroscopic ACL reconstruction:
Arthroscopic ACL reconstruction is a technically demanding procedure and surgical precision is imperative for perfect restoration of anatomy and function. Computer navigation-aided arthroscopic ACL reconstruction ensures 100 per cent accuracy and enables precise surgery with superior functional outcome. KDAH is the first and the only hospital in India (and one of only 18 in the world) to offer computer navigationaided arthroscopic knee ligament reconstruction. - Arthroscopic PCL surgery:
With advances in surgical technique and arthroscopic instrumentation, posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) injuries are also now managed with arthroscopy. The author has pioneered an innovative arthroscopic procedure for PCL tibial bony avulsion repair that is internationally accepted as the treatment of choice for these injuries. - Meniscus preservation surgery:
Today, the importance of the meniscus to knee function, especially load transmission and peripheral stability, is increasingly recognised. Every effort is made not to resect torn menisci, but instead repair and, if necessary, replace them via transplantation. - Autologous chondrocyte transplantation:
Articular cartilage injuries do not heal and traditional cartilage restoration procedures result in an inferior fibrocartilage repair. Autologous chondrocyte transplantation (ACT) is the only technique that reproduces natural hyaline cartilage even in large osteochondral defects. The first ACT in India was performed at KDAH and this institution is considered the nation’s leading cartilage repair centre. - Arthroscopic shoulder stabilisation:
Recurrent shoulder dislocations and other instability patterns are extremely disabling not only for athletes but also for any active individual. Advances in arthroscopic instrumentation and bio-absorbable implants have ensured that arthroscopic repair of shoulder instability has excellent outcome and, unlike open shoulder surgery, it does not result in postoperative restriction of movements. - Arthroscopic rotator cuff “footprint” repair:
The rotator cuff is a musculotendinous envelope around the shoulde. When torn, it can result in severe pain, weakness, and disability. Until recently, it was repaired with an open approach or arthroscopic single-row/double-row anchor technique. Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair using the latest generation anchors that restore the anatomic rotator cuff footprint have resulted in outcomes far exceeding the earlier procedures and were first introduced in India at KDAH. - Hip arthroscopic management for femoroacetabular impingement (FAI):
Acetabular labral tears and FAI have been increasingly identified as a source of pain and disability in young adults. Hip arthroscopy is the ideal approach to treat these lesions. KDAH is internationally recognised as one of the few centres of excellence for hip arthroscopic surgery. - Ankle and elbow arthroscopy for sports injuries:
The advent of arthroscopy for the ankle and elbow joints has revolutionised the treatment of injuries to these joints. Individuals with cartilage defects, ligament tears, loose bodies, stiffness and impingement syndromes, can often return to their highest capabilities in the shortest possible time. - Musculotendinous endoscopy:
Muscle and tendon problems such as tennis elbow, heel pain, and Achilles tendon strains are common. Recent advances in laser and radiofrequency technology have made endoscopy the ideal minimally invasive method to treat these chronic injuries.
What is arthroscopy?
Arthroscopy is a surgical procedure used by orthopaedic surgeons to visualise, diagnose, and treat problems of joints. The word arthroscopy comes from two Greek words, “arthro” (joint) and “skopein” (to look). The term literally means “to look within the joint.”
Modern and minimally invasive
In an arthroscopic surgery, an orthopaedic surgeon makes a small puncture in the patient’s skin and then inserts a fine telescope into the joint. This transmits a magnified image of the patient’s joint to a monitor, allowing the surgeon to thoroughly evaluate the joint, determine the amount or type of injury and then repair or correct the problem with specially designed instruments that are inserted through additional punctures.
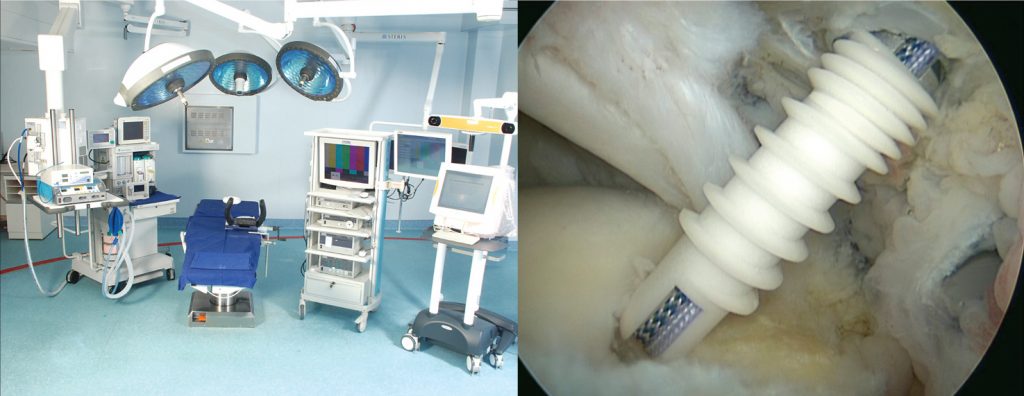
The arthroscopy and sports orthopaedics service at kdah provides state-of-theart treatment for joint problems using minimally invasive endoscopic techniques.
The services offered include:
Knee arthroscopy
- Knee ligament reconstructive surgery
- computer navigated arthroscopic ACL reconstruction
- arthroscopic PCL reconstruction
- multiple ligament reconstruction for dislocations
- Meniscus surgery
- meniscus repair
- partial menisectomy
- meniscus transplants
- Articular cartilage repair
- mosaicplasty / osteochondral autograft transfer
- synthetic osteochondral implants
- autologous chondrocyte transplantation
- osteochondral transplants
- radiofrequency / laser chondroplasty
- Patellofemoral instability surgery
- MPFL repair and reconstruction
- Proximal and distal realignment surgery
- Arthroscopy for synovial pathology
- Arthroscopy for painful total knee replacements
- Computer navigation corrective osteotomy for malalignment
Shoulder arthroscopy
- Shoulder instability repair for recurrent dislocations
- arthroscopic Bankart repair
- reconstructive surgery for bony deficiencies
- Shoulder problems in throwing athletes
- arthroscopic SLAP repair
- arthroscopic biceps tenodesis
- arthroscopy for acromioclavicular joint problems
- arthroscopy for impingement syndromes
- Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair
- Arthroscopic management for frozen shoulder
- Shoulder reconstructive surgery for fractures
- Shoulder replacements including surface arthroplasty
Advanced arthroscopic reconstructive surgery
- Hip arthroscopy
- Labral tears & femoroacetabular impingement
- Loose body removal
- Synovectomy
-
Ankle arthroscopy
- Sports injuries & ligament tears
- Bony & soft tissue impingement
- Cartilage defects and osteochondritis dissecans
- Fusion for arthritis
- Arthrolysis for stiff ankles
-
Elbow arthroscopy
- Sports injuries and ligament tears
- Stiff elbow release
- Loose bodies & capitellar osteochondritis
- Synovectomy
- Tennis elbow release
- Wrist arthroscopy
- Muscle & tendon endoscopic surgery
- Bone endoscopic surgery
 Back to Site
Back to Site