A Cornerstone in the Management of Gait Disorders
Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital’s Gait and Motion Analysis Laboratory is the first of its kind in Mumbai. The laboratory is fundamental to the treatment of patients with orthopaedic (bone and joints) and neuromuscular (nerve and muscle) disorders
anagement of gait and motion has advanced significantly in the past few years. This includes diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation, which has enabled development of sports medicine and has also helped patients with many other orthopaedic and neurological disorders. An individual needs efficient movement of flexible joints, strong muscles and a balance between different muscle groups. If these are not optimal, the individual has an abnormal gait and is prone to injuries. Gait and motion analysis has helped doctors find the cause for many of these limb problems. An assessment of the way an individual walks and runs gives in-depth insight about the body biomechanics, weight distribution and relative movement of hips, knees and ankles during these activities. Gait and Motion Analysis acts as a diagnostic as well as a monitoring tool. It allows clinicians to objectively measure gains that are achieved following proper medical or surgical intervention. With its help, a physician can determine which surgical approach is the best option.
Gait and upper limb analysis are fundamental to the treatment of patients with orthopaedic (bones and joints) and neuromuscular (nerve and muscle) disorders. The Gait and Motion Analysis Laboratory provides comprehensive patient reports for physiatrists, orthopaedic surgeons, neurologists, paediatricians, podiatrists, physical therapists and other specialists.
Clinical gait analysis is performed to allow selection from amongst different available treatment options. This is based on a number of factors that are taken into consideration: Underlying cause of the problem (diagnosis of the disease entity); assessment of the severity, extent or nature of a disease or injury; monitoring progress in the presence or absence of an intervention; and prediction of the outcome of an intervention. Gait analysis can be observational or instrumented in nature. Observational Gait Analysis can measure some temporal and spatial parameters of the gait cycle; it is subjective and does not offer sensitive, reliable, repeatable and valid quantifications of the gait parameters. On the other hand, instrumented gait analysis measures temporal and spatial parameters of gait, as well as the kinematics, kinetics and dynamic EMG of relevant gaitspecific muscle-joint mechanisms.
The Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital Gait and Motion Analysis Laboratory is a large room equipped with infrared cameras, video cameras force plates and telemetric EMG. India’s first of its kind in a corporate set-up, the system consists of simultaneous data acquisition and analysis of four components: six infra red optical cameras capturing human motion in space, 16 channel telemetric EMG representing muscle activity, two force plates measuring joint angles and forces, and two video cameras capturing video in sagittal and coronal plane..
The steps for assessing gait and motion involve:
- Patient Preparation (30 minutes) includes changing into appropriate clothing, with anthropometric measurements, marker placements and EMG electrode placement.
- Data Capture (60-90 minutes) includes calibration, standing trial and walking trials.
- Tracking & Elaboration (60 minutes) includes tracking of markers [manual / auto] and elaboration to select good cycles.
- Interpretation is simultaneous integration of four parameters which is a time-unlimited.
Gait and Motion Analysis is an important advancement in the field of sports medicine and rehabilitation. This technology is widely available in the West and is being increasingly used in everyday practice. Gait and Motion Analysis is useful in a number of different clinical situations:
- It helps identify muscles for intervention and surgical procedures in children with cerebral palsy; it also reduces the frequency of surgical procedures and ensures higher positive outcomes.
- It evaluates changes in the walking ability of Parkinson’s disease patients, and for quantifying the improvements.
- It’s also a useful tool in assessing spastic gait deviations and targeting muscles for intervention and to evaluate gait asymmetry in stroke.
- It helps evaluate gait impairments and planning of intervention in Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus.
- It assesses gait dysfunctions in patients with traumatic brain injury and, therefore, helps plan appropriate corrective strategies.
- It helps in correct fi tment/alignment of lower limb prosthesis and assesses need for orthotics/splints in neurological and orthopaedic problems.
- This assessment is preventive and curative in athletes in various conditions like plantar fasciitis, heel spur, fl at feet, morton’s neuroma, hammer toe, shin splints, knee pain, chronic back pain, calf stiffness etc.
Features of Gait and Motion Analysis
- Temporal
Stance and swing phase duration with stride time and cadence - Distance
Step and stride length, step width and gait velocity - Kinematics
Motion at different joints in space - Kinetics
Force / torque and power at different joints producing these movements - Electromyography
Muscle activity producing these joint forces

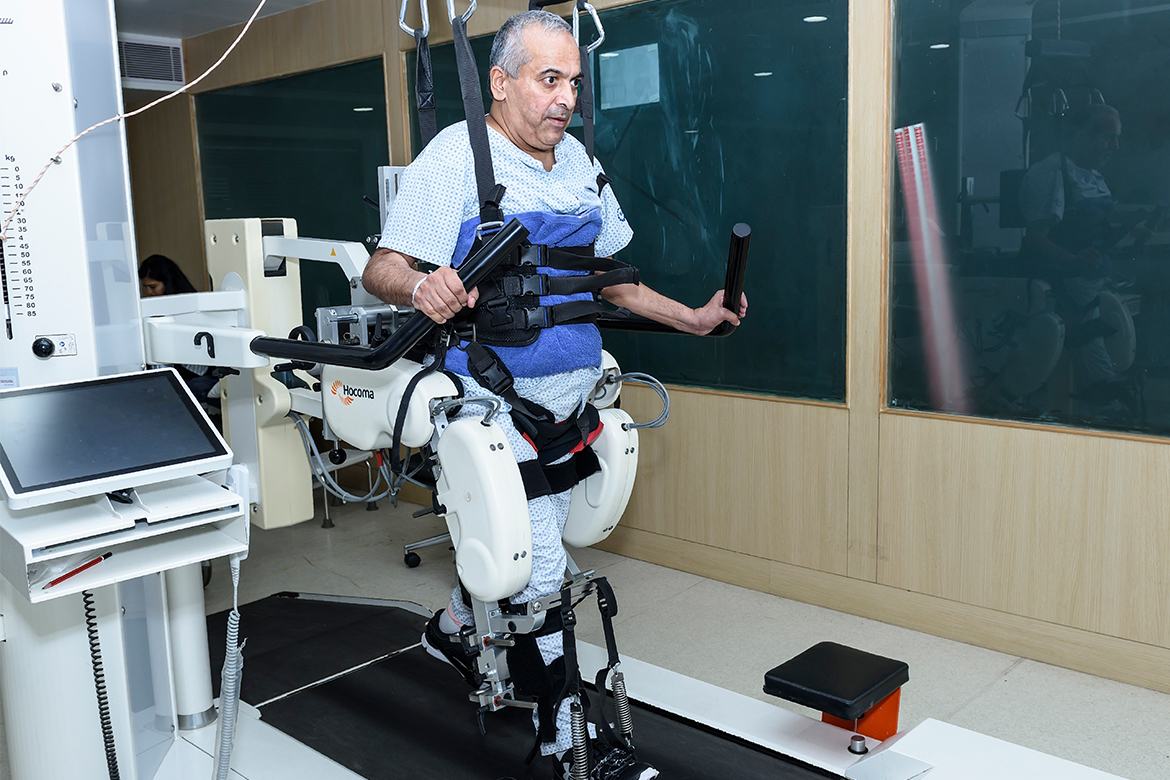
Key Technology for rehabilitation at KDAH
- Multi-joint Dynamometer with Work Simulator:
The multi-joint dynamometer can measure muscle strength of any major muscle group. Work simulator can simulate many activities like driving or plumbing, and aids in the evaluation of functional capacity and disability assessment. This assessment helps in making a rehabilitation programme and strength training schedule for patients with sports or other injuries, specifi cally targeting isolated weaker muscle groups - Balance Assessment and Training System (BATS):
This system helps in assessing the balance capabilities of a sportsman and evaluates the underlying cause of impaired balance in patients with sports injuries. Balance Master is both a useful diagnostic and therapeutic training tool and aids in evaluating the underlying cause of impaired balance in patients with neurological illness like stroke, Parkinson’s disease, peripheral neuropathy or vertigo and sports injuries. - Video Nystagmography (VNG):
VNG is a clinical study used to evaluate patients with dizziness, vertigo, or balance dysfunction. - Body-Weight Support Treadmill Gait Training System (BWSTT):
Treadmill therapy with partial Body Weight Support is a promising new approach to improve gait ability after stroke. - EMG Biofeedback:
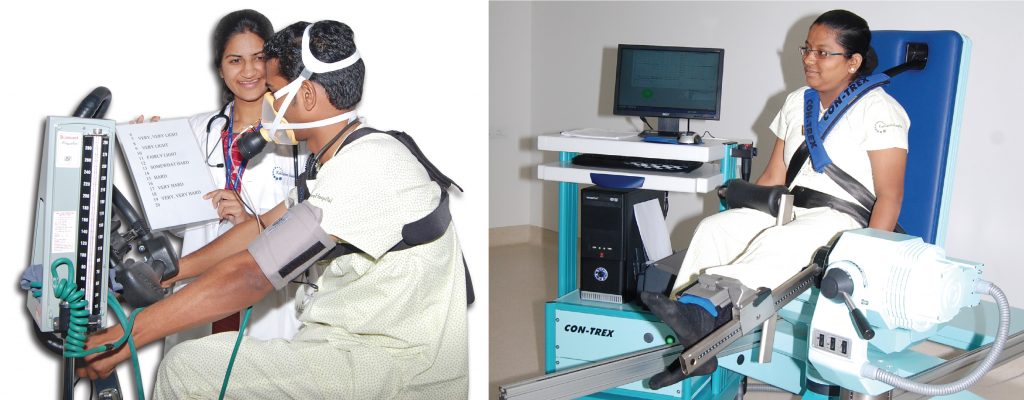
EMG Biofeedback produces rapid and signifi cantly greater strength when combined with more traditional forms of strength training. It is used for muscle re-education and strengthening in stroke patients, rehabilitation following surgery or trauma, selective training of a particular muscle after injury and to remediate neck, scapular and lower back pain. - Human Performance Evaluation (VO2 max):
The measurement of VO2 max (maximum aerobic capacity) helps in planning cardiopulmonary and sports rehabilitation programmes and refl ects the overall physical fi tness of the individual. It involves a graded exercise test (either on treadmill or cycle ergometer) in which exercise intensity is progressively increased while measuring ventilation and oxygen and carbon dioxide concentration of the inhaled and exhaled air.
 Back to Site
Back to Site